Real Time Images of the Sun
SOHO EIT 304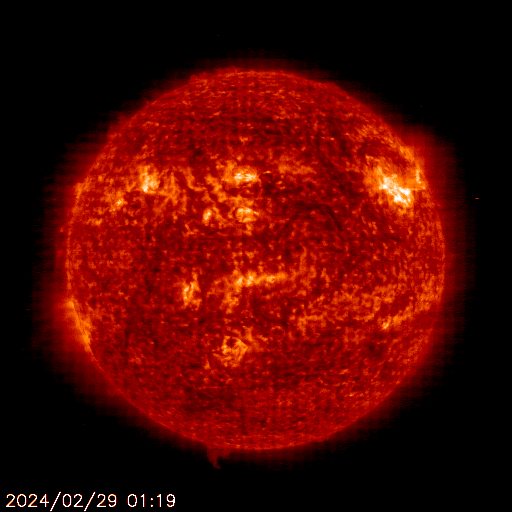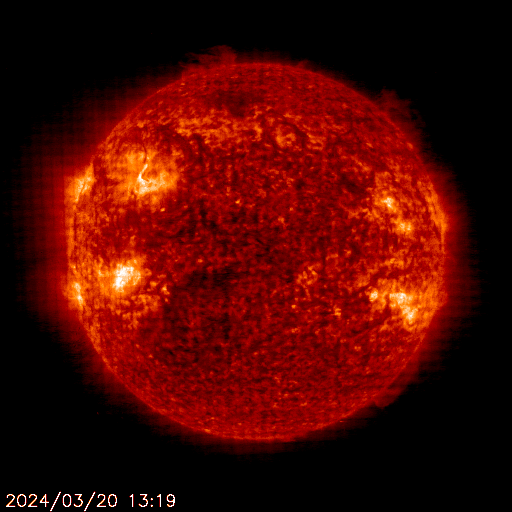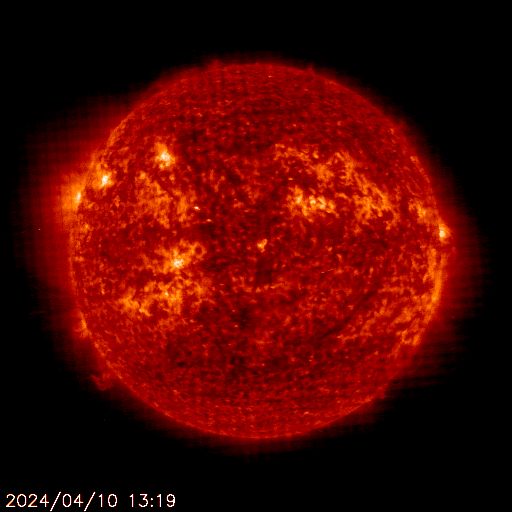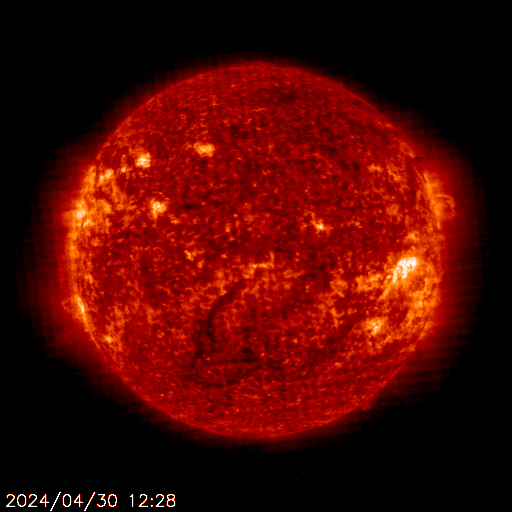
|
SOHO EIT 284 Animated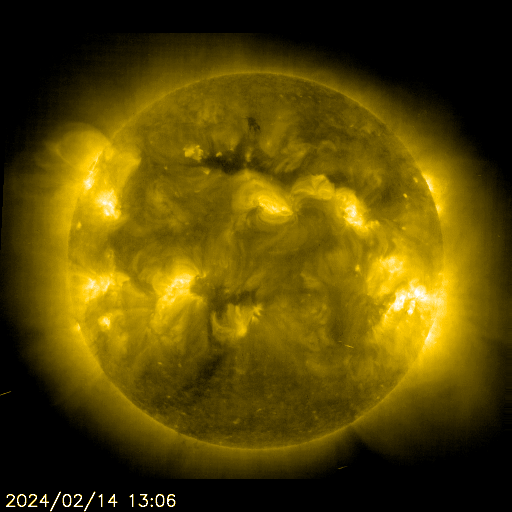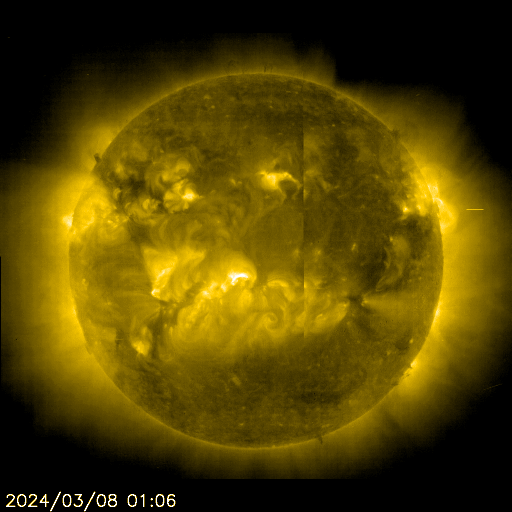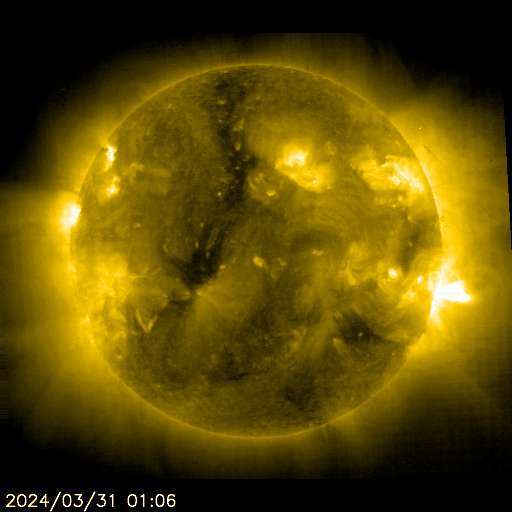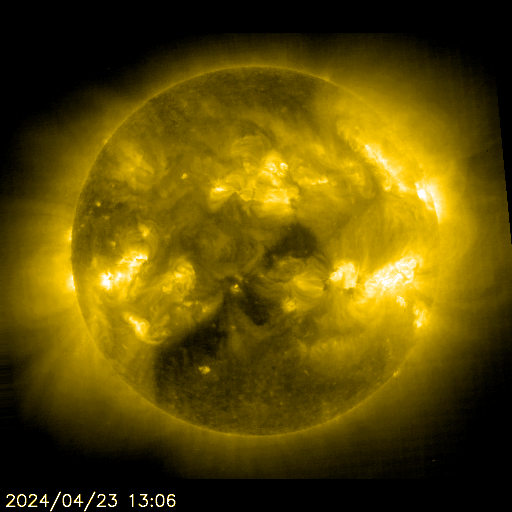
|
LASCO/C2
|
The sun is constantly monitored for sun spots and coronal mass ejections. EIT (Extreme ultraviolet Imaging Telescope) images the solar atmosphere at several wavelengths, and therefore, shows solar material at different temperatures. In the images taken at 304 Angstrom the bright material is at 60,000 to 80,000 degrees Kelvin. In those taken at 171 Angstrom, at 1 million degrees. 195 Angstrom images correspond to about 1.5 million Kelvin, 284 Angstrom to 2 million degrees. The hotter the temperature, the higher you look in the solar atmosphere.
Solar activity continued at low levels. Flaring was limited to isolated C- and B-class flares. The C-class flares were produced by Region 4384 (N09E33, Eho/beta) and the plage of decayed Region 4380 (S21, L=205). X-ray background flux subsided below the C-level. Region 4378 (N16W22, Cso/beta) gained a companion pore just south of its leader spot. The trailing spots of Region 4381 (N08E09, Cao/beta) decayed throughout the period, including loss of penumbra. Region 4384 remains the largest group on the disk, but exhibited further simplification as its intermediate spots dissipated and its primary trailing spot decreased in size. A new region 4385 (S08E24, Bxo/beta) emerged in the southeast as a stable but unremarkable collection of small pores. No Earth-directed CMEs were observed in available coronagraph imagery.
Solar Activity Forecast
Issued: 2026 Mar 05 1230 UTC
Solar activity is expected to be at low levels, with a slight chance for isolated M-class activity (R1-R2/Minor-Moderate) through 07 Mar. Energetic
Real Time Solar X-ray and Solar Wind
Solar Cycle Progression
Solar Cycle chart updated using the latest ISES predictions. |
Real-Time Solar Wind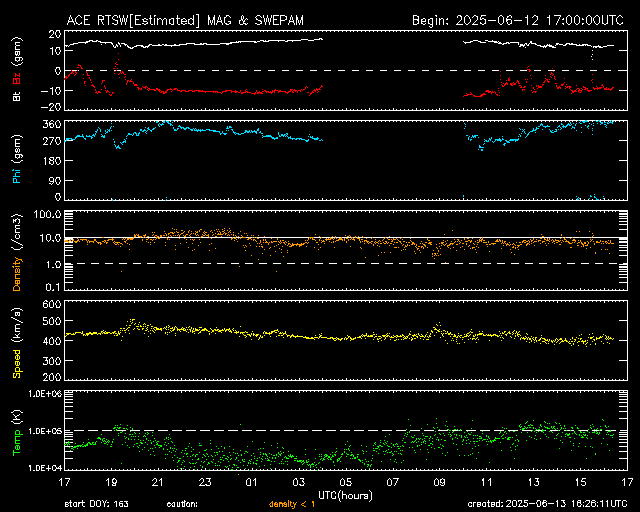
Real-Time Solar Wind data broadcast from NASA's ACE satellite. |
The Solar Cycle is observed by counting the frequency and placement of sunspots visible on the Sun. Solar minimum occurred in December, 2008. Solar maximum is expected to occur in May, 2013.
Solar X-ray Flux This plot shows 3-days of 5-minute solar x-ray flux values measured on the SWPC primary and secondary GOES satellites. |
Satellite Environment Plot The Satellite Environment Plot combines satellite and ground-based data to provide an overview of the current geosynchronous satellite environment. |
Auroral Activity Extrapolated from NOAA POES
Northern Hemi Auroral Map
|
Southern Hemi Auroral Map
|
Instruments on board the NOAA Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) continually monitor the power flux carried by the protons and electrons that produce aurora in the atmosphere. SWPC has developed a technique that uses the power flux observations obtained during a single pass of the satellite over a polar region (which takes about 25 minutes) to estimate the total power deposited in an entire polar region by these auroral particles. The power input estimate is converted to an auroral activity index that ranges from 1 to 10.
Credits:
Space Weather Images and Information (excluded from copyright) courtesy of: NOAA / NWS Space Weather Prediction Center, Mauna Loa Solar Observatory (HAO/NCAR), and SOHO (ESA & NASA).Space Weather links:
3-Day Forecast of Solar and Geophysical Activity
Space Weather Now
Real-Time Solar Wind
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
The Very Latest SOHO Images